Oracle provides three different applications along with licensing options for Business Intelligence and Data warehousing. Those tools are: Oracle Discoverer 10g (Oracle BI Suite Standard Edition), Oracle Business Intelligence Standard Edition One (for mid-market segment) and Oracle BI Suite Enterprise Edition (formerly Siebel Analytics).
This article shows the purpose and major characteristics of each of the Oracle BI applications, also indicating similarities to IBM Cognos 8 and SAP Business Objects applications.
This article shows the purpose and major characteristics of each of the Oracle BI applications, also indicating similarities to IBM Cognos 8 and SAP Business Objects applications.
ORACLE DISCOVERER 10G (ORACLE BI SUITE STANDARD EDITION) QUERY & ANALYSIS
Oracle Discoverer is an ad-hoc query and analysis tool which allows users to do basic query construction along with tables, cross tabs and charts. End users can interactively navigate, drill down, slice and dice, aggregate and add calculations. It is very commonly used with Oracle RDMBS (most likely with the OLAP database option) and embedded in a number of Oracle Applications in the Oracle e-Business Suite.
In 2006 Oracle Discoverer was repackaged along with Oracle Reports, BI Beans and other tools to form Oracle BI Standard Edition.
The main advantages of Discoverer are Personalized Portals where worksheets can be customized at the portal level for each user, the fact that it comes in a bundle which affects its price and its technology infrastructure is generally very well received by IT.
The problem with Discoverer is that its future is rather uncertain and it should be rather considered as a legacy product. Among other weaknesses it is worth mentioning that it is Oracle only (only Oracle native connection, no multiple data sources, other RDBMS via ODBC only) and its reporting capabilities are limited to singly block (only one graph/crosstab/table).
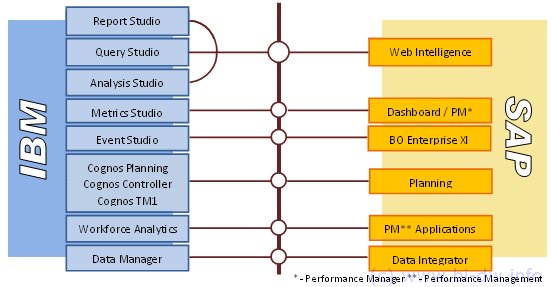
Discoverer competes with Query Studio, Analysis Studio, Report Studio (for IBM Cognos 8) and SAP BusinessObjects Web Intelligence and Desktop Intelligence.
In 2006 Oracle Discoverer was repackaged along with Oracle Reports, BI Beans and other tools to form Oracle BI Standard Edition.
The main advantages of Discoverer are Personalized Portals where worksheets can be customized at the portal level for each user, the fact that it comes in a bundle which affects its price and its technology infrastructure is generally very well received by IT.
The problem with Discoverer is that its future is rather uncertain and it should be rather considered as a legacy product. Among other weaknesses it is worth mentioning that it is Oracle only (only Oracle native connection, no multiple data sources, other RDBMS via ODBC only) and its reporting capabilities are limited to singly block (only one graph/crosstab/table).
Discoverer competes with Query Studio, Analysis Studio, Report Studio (for IBM Cognos 8) and SAP BusinessObjects Web Intelligence and Desktop Intelligence.
ORACLE BI SUITE ENTERPRISE EDITION (SIEBEL ANALYTICS)
After acquiring Siebel in February 2007, Oracle decided to use Siebel Analytics as a key component of their Business Intelligence strategy and the product was renamed to Oracle BI Suite Enterprise Edition (OBI EE).
Oracle’s vision is to continue to focus their Business Intelligence efforts on Enterprise Edition after the acquisition of Hyperion.
Oracle’s vision is to continue to focus their Business Intelligence efforts on Enterprise Edition after the acquisition of Hyperion.
- Oracle BI Enterprise Edition (OBI EE) consists of:
- Oracle BI Server - BI server and common enterprise semantic layer, it provides ROLAP and federated data queries
- Oracle BI Answers - Ad-hoc query and reporting. It uses a central repository (a semantic layer)
- Oracle BI Interactive Dashboards – dashboarding solution and a way to distribute Oracle BI Answers reports
- Oracle BI Delivers - Business activity monitoring (BAM) and alerting solution
- Oracle BI Disconnected Analytics - mobile analytics
- Oracle BI Publisher (formerly known as XML Publisher) - Enterprise reporting and distribution of "pixel-perfect" reports
- Oracle BI Briefing Books – creates snapshots of dashboard pages for offline use
Oracle BI suite EE Answers and Dashboards products compete with Cognos Query Studio, Analysis Studio, Report Studio and SAP BusinessObjects Web Intelligence (along with Web Intelligence Rich Client). Oracle Interactive Dashboards are equivalent to IBM Cognos 8 Go!Dashboard and a lightweight version of BusinessObjects Dashboard Builder or Crystal Xcelsius.
ORACLE BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE STANDARD EDITION ONE MID-MARKET
Introduced in June 2007, Oracle BI Standard Edition One (OBI SE1) is a packaging of Business Intelligence and data warehouse products aimed at providing a complete solution for the mid-market (5-50 named users).
Oracle Business Intelligence Standard Edition One is a subset of Oracle BI Enterprise Edition(previously Siebel Analytics) containing basic functionality like dashboarding, ad hoc querying and pixel perfect static reporting, and also data integration and database technology.
Oracle Business Intelligence Standard Edition One is a subset of Oracle BI Enterprise Edition(previously Siebel Analytics) containing basic functionality like dashboarding, ad hoc querying and pixel perfect static reporting, and also data integration and database technology.
- OBI SE1 includes the following applications:
- Oracle BI Dashboards –dashboarding providing the ability to combine ad hoc and pixel perfect reports, provide links between them and a drill through functionality.
- Oracle BI Answers – Ad-hoc query with analysis limited to drilldown.
- Oracle BI Publisher – Reporting tool to create and distribute pixel-perfect formatted reports.
- Oracle Warehouse Builder (OWB) – An ETL tool bundled with Oracle RDMS.
- Oracle Database Standard Edition One – a database offering packaged and priced for small-to-medium businesses or departmental systems providing full database functionality (limited to 2 CPU).
- OBI SE1 doesn't include the following Enterprise Edition capabilities:
- Alerts (e-mail distribution, alerts)
- Disconnected Analytics (offline dashboards and querying)
- MS Office Plug-in
Strengths and Weaknesses
- Key strengths of OBI SE1 are:
- It is a complete solution including database – the package provides Business Intelligence tools for reporting, analysis, as well as ETL and a database to act as a data warehouse.
- Low entry price (up to 50 named users)
- Multiple data source semantic layer - can combine multiple, different data sources.
- For those familiar with Oracle Discoverer, they will find OBI SE1 to be a better option for query, dashboarding and reporting.
However, OBI SE1 is still an Oracle focused solution (for reporting and ETL target it must be an Oracle RDBMS, MS SQL Server, IBM DB2 and Teradata can be used as ETL sources) and as a mid-market solution it cannot be run at more than 50 named users (when deployment goes beyond 50 named users the customer needs to move to Enterprise Edition). There is also no support for Linux as Oracle Business Intelligence Standard Edition One runs on the Windows 2000 or Windows 2003 server only.
OBI SE1 competes primarily against IBM Cognos 8 BI and Business Objects Professional products family.